🧶
[프로그래머스] 게임 맵 최단거리
February 03, 2023
1. 문제
프로그래머스
2. 핵심 아이디어
BFS
3. 코드
[swift]
import Foundation
func solution(_ maps: [[Int]]) -> Int {
var maps = maps
let n = maps[0].count
let m = maps.count
let dx: [Int] = [0,0,-1,1]
let dy: [Int] = [1,-1,0,0]
var queue: [(Int, Int)] = []
queue.append((0,0))
maps[0][0] = 1
while !queue.isEmpty {
let element = queue.removeFirst()
let x = element.0
let y = element.1
for i in 0...3 {
let dx = x + dx[i]
let dy = y + dy[i]
if dx >= 0 && dx < n && dy >= 0 && dy < m {
if maps[dy][dx] == 0 {
continue
}
if maps[dy][dx] == 1 {
maps[dy][dx] = maps[y][x] + 1
queue.append((dx,dy))
}
}
}
}
return maps[maps.endIndex - 1][maps.endIndex - 1] == 1 ? -1 : maps[maps.endIndex - 1][maps.endIndex - 1]
}[python]
from collections import deque
def solution(maps):
n = len(maps[0])
m = len(maps)
direction = [(0,1), (0,-1), (1,0), (-1,0)]
dq = deque()
dq.append((0,0))
maps[0][0] = 1
while dq:
x,y = dq.popleft()
for direct in direction:
dx = x + direct[0]
dy = y + direct[1]
if 0 <= dx < n and 0 <= dy < m:
if maps[dy][dx] == 0:
continue
if maps[dy][dx] == 1:
maps[dy][dx] = maps[y][x] + 1
dq.append((dx,dy))
return maps[-1][-1] if maps[-1][-1] != 1 else -14. 풀이 과정
흔히 보던 BFS/DFS 탐색 문제였다!
BFS로 아직 탐색하지 않은 경로 (maps[dx][dy] == 1 인 경우) 와 벽을 피해주면서 탐색하면 되었다.
그렇게 쉽게 문제를 푼 다음, DFS로도 문제를 풀어보려 했었는데…
DFS 로는 문제가 풀리지 않았다.
[python]
def solution(maps):
n = len(maps[0])
m = len(maps)
direction = [(0,1), (0,-1), (1,0), (-1,0)]
def DFS(x,y):
if x == n - 1 and y == m - 1:
return
for direct in direction:
dx = x + direct[0]
dy = y + direct[1]
if 0 <= dx < n and 0 <= dy < m:
if maps[dy][dx] == 0:
continue
if maps[dy][dx] == 1 or maps[y][x] + 1 < maps[dy][dx]:
maps[dy][dx] = maps[y][x] + 1
DFS(dx,dy)
DFS(0,0)
return maps[-1][-1] if maps[-1][-1] != 1 else -1이 DFS 코드가 실패하는 이유는 탐색하는 경로가 너무나 많아지기 때문이다.
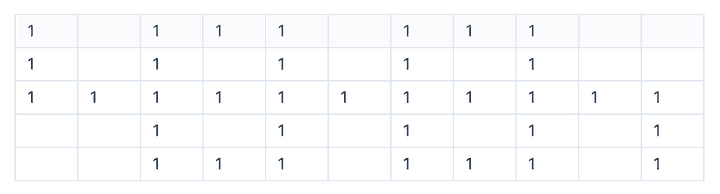
이런 형태의 맵이 있다고 가정한다면,
DFS는 교차로 (위, 오른쪽, 아래쪽) 를 모두 3^n * k (n는 삼거리의 개수, k는 삼거리의 경로 개수) 연산으로 탐색을 해야하기 때문에… 시간복잡도가 망하는 것이였다.
이처럼 문제에서 최단 거리를 제공한다면 (마지막 종착지가 정해져있고 가중치가 없음) BFS가 확실히 좋은 선택이다 라고 느꼈다.